

Introduction :
The Medical Industry has always been a complicated and evolving one but the 21st century transforms the borders of reality and imagination through medical Augmented Reality. Augmented reality AR is becoming a game changer in healthcare. It brings together the digital environment with the real one. Digital content such as 3D models, photos, and sounds are all integrated as we enjoy better and more interactive experiences.
In this blog, we will delve into the use of augmented reality in healthcare and see how it is transforming the medical field beyond recognition. If you’re curious and eager to discover more related to the subject of augmented reality and its impact on healthcare, make sure to continue reading and learning more!

1. Augmented Reality (AR)
- Augmented Reality (AR) is an interactive experience that allows the real world to fuse with the virtual world to create 3D content. These include things such as images, sounds, and other sensing methods. AR uses computer hardware that consists of applications, consoles or screens, or projections to achieve the blend between the virtual information space with the environment around the real world.
- Augmented Reality in healthcare translates to the application of digital images in the surrounding physical environment. The main objective is often to demonstrate inside or outside body parts to teach students, treat psychological trauma, and re-educate professionals.
- Research across the globe shows that augmented reality in healthcare is currently generating revenue of about $525 million and is expected to rise rapidly and reach a total valuation of $1,565 million according to the Research Dive report.

2. Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality
- AR uses real-life surroundings while VR is an entirely virtual world.
- Through AR, users can regulate their virtual presence in the real world, whereas VR users are mostly under the control of systems themselves.
- VR requires a headset gear, but AR can be accessed via cell phone.
- AR will make sure that both the digital and the real world are improved, and VR will only give a fictional world.
3. Applications of Augmented Reality
In the healthcare sector, AR has many applications spread over multiple areas such as disease management, patient education and surgical training. Imagine that surgeons will soon be able to visualize the 3D models shown up on the operating table using the optical head-up system (smart glasses/goggles). Also, medical students will learn about human anatomy in a new way through AR/VR immersive experiences with the help of AR glasses while not using physical specimens.
3.1 AR Surgery
In the field of surgery, the integration of enhanced reality has been effective in a variety of procedures, which has boosted the standards of treatment and the outcome of the surgical procedures.
- The AR navigation systems afford different advantages to surgeons and patients.
3.2 Interactive Medical Training
Virtualization of AR- facilitated training offers a more profound understanding of the complexities of the body system and allows practitioners to deal appropriately with extreme cases in a limited time.

3.3 Telehealth & Proctoring
In Telehealth, AR can help doctors with assisted diagnosis by allowing them to deliver explanatory visuals and data through a device such as a smartphone and give patients important information.
- Proctoring in medicine has been around for a long time where the medical practitioner guides and supervises a colleague surgeon or dentist during a procedure.
- AR proctoring provides the prospect of sending a specialist to another hospital virtually “scrubbing in” with an AR headset.
3.4 Remote Guidance
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) can play a crucial role in remote guidance by analyzing data feeds from the surgeon and patient during a procedure and assisting customers & employees who need assistance as if they were on-site.
- By making use of visual resources such as Augmented Reality that enable two people to work together and solve issues in real-time, communication becomes more streamlined compared to just words being used as a means of expression.
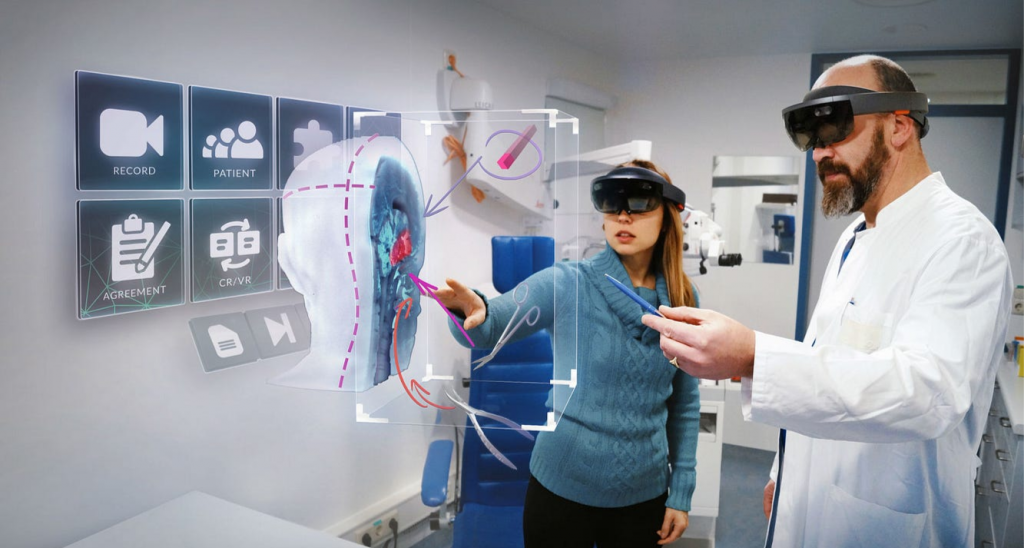

4. Challenges of AR in Healthcare
4.1 Cost and Accessibility
- AR technology including headsets and specialized glasses is the costliest hardware. It may be because small healthcare organizations might not be ready to follow it and some areas may be deprived of such services in terms of economic status.
- As technology continues to evolve, the price of augmented reality equipment will likely go down, while more healthcare providers and patients will have access to this technology.
4.2 Data Privacy & Security
- AR applications in healthcare usually process highly confidential information about the patient, for example, the collection of medical scans and vital signs.
- Strong security mechanisms will greatly reduce the risks of leaks and care for the patient’s privacy.
4.3 Regulatory Barriers & Ethics
- The dynamic regulations in the AR healthcare space are going through some radical changes.
- Creating regulations that protect user data, devices, and application development processes should be one of the top priorities to make sure the technology is implemented mindfully.
4.4 Managing AR Devices
- Implementing AR devices in healthcare workflow systems needs to be done smoothly and this can be realized using proper device management methods.
- This includes developing a user protocol, implementing EMR connections, creating charging and disinfectant protocols, and providing regular training for the staff.
5. Future of AR in Healthcare
Healthcare workers realize the advantages of Augmented Reality (AR) technologies very early. The future of AR in healthcare is exciting with prospects such as gamified physical therapy and virtual dental hygiene enlightening the patients and bringing revolution in medical training.
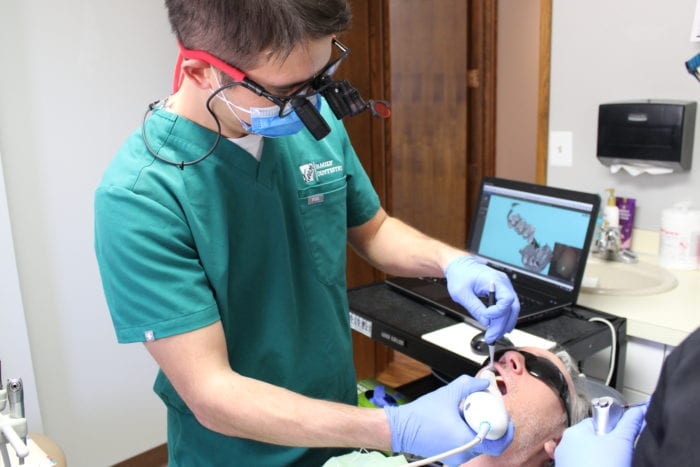
5.1 AR in Dental Practice
- AR also helps dentists place brackets in orthodontics through 3D image-based tooth tracking.
- The ability of AR to enhance spatial visual perception will go a long way in pre-clinical practices, such as designing treatment cavities for students’ analysis and learning.
5.2 AR for Psychomotor Skills Training
- AR training tools blur the physical and digital worlds to facilitate spatial and psychomotor skills training in the medical domain. While using this technology, learners will be interacting with virtual objects which are superimposed directly on their surroundings.
- Learners get real-time feedback leading to learning positive AR experiences. In future, AR will increase the scope of self-directed skills-based training, improving skill acquisition and retention.
5.3 AR to Gamify Workout Sessions
- AR may reduce costs significantly, save thousands of lives and upgrade our standard of living significantly.
- Even if you work out at home, you still have a chance to join a digital workout group with other people using AR apps like FitTech.

6. Real-life Examples of Augmented Reality
Here are some examples of the AR, which is already improving healthcare, by helping surgeons and supporting patients.
6.1 Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, allows doctors to manipulate a broader variety of complex operations using greater precision, flexibility, and control than before.
- Mostly, a robotic surgery system includes a camera arm and mechanical arms with surgical instruments fastened on them.
- For the surgeon, magnified high-definition and 3D views of the surgical site appear as if they were extracted from a 3D printer.
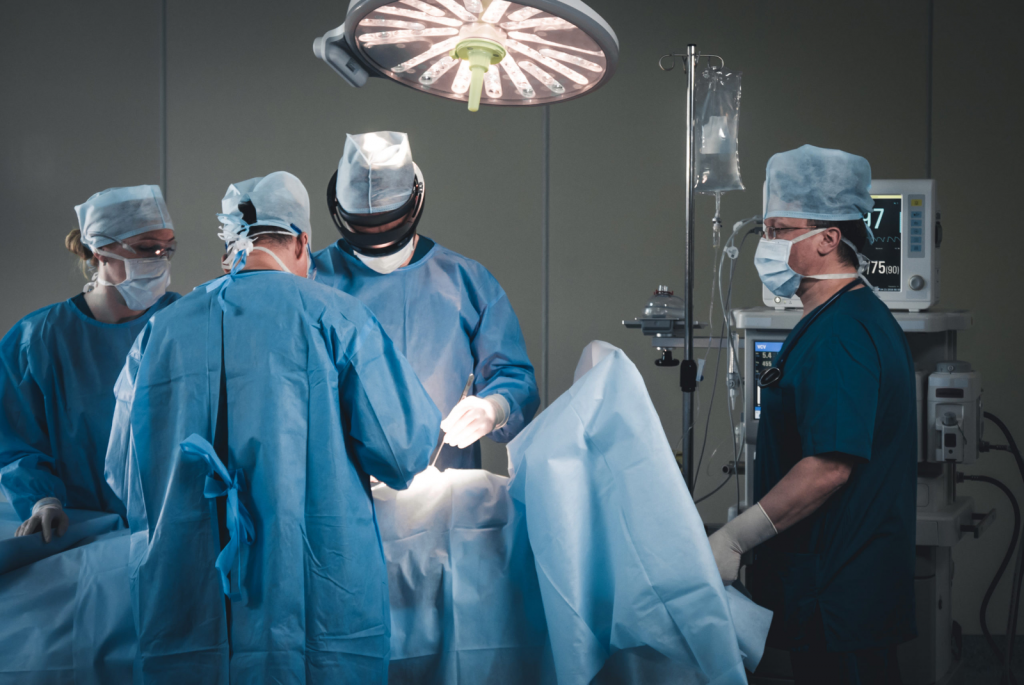
6.2 Advanced Wound Care Surgery
- Augmented reality (AR) has the potential to revolutionize wound care surgery, offering both surgeons and patients significant benefits.
- Imagine surgeons wearing AR headsets that project detailed 3D models of the wound bed directly onto the surgical field.
- This overlay could highlight underlying structures like blood vessels and nerves, allowing for Increased Precision and Reduced Complications
The application of Augmented Reality (AR) in healthcare has experienced its highs and lows. Ranging from increasing surgical accuracy to gamifying physical therapy, AR can potentially change multiple faces of healthcare. As AR becomes more accessible and secure, we will see more new applications that will change the healthcare landscape for patients and practitioners. Through this technology, we can create a more efficient, effective, and patient-oriented healthcare system.
Recents Post


3D Product Visualization in Modern Marketing

Augmented Reality in Healthcare

XR Games : The Next Frontier of Entertainment

Boosting Marketing Strategies with 3D Product Animation

